MEAN
MEAN
The mean is the average of the numbers. It is easy to calculate: add up all the numbers, then divide by how many numbers there are. In other words it is the sum divided by the count.
Types of means
Pythagorean mean
Arithmetic mean (AM)
The arithmetic mean (or simply mean) of a list of numbers, is the sum of all of the numbers divided by the number of numbers. Similarly, the mean of a sample , usually denoted by , is the sum of the sampled values divided by the number of items in the sample
For example, the arithmetic mean of five values: 4, 36, 45, 50, 75 is:
- Geometric mean (GM)
The geometric mean is an average that is useful for sets of positive numbers, that are interpreted according to their product (as is the case with rates of growth) and not their sum (as is the case with the arithmetic mean):
For example, the geometric mean of five values: 4, 36, 45, 50, 75 is:
Harmonic mean (HM)
The harmonic mean is an average which is useful for sets of numbers which are defined in relation to some unit, as in the case of speed (i.e., distance per unit of time):
For example, the harmonic mean of the five values: 4, 36, 45, 50, 75 is
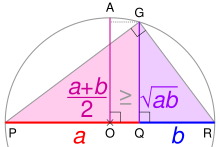
Relationship between AM, GM, and HM
AM, GM, and HM satisfy these inequalities:
Equality holds if all the elements of the given sample are equal.
METHOD TO FIND MEAN

 ,
,


![{\displaystyle (4\times 36\times 45\times 50\times 75)^{\frac {1}{5}}={\sqrt[{5}]{24\;300\;000}}=30.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3b516046ef2a7b8b23301b7ab228cec73f38e062)







Knowledgeable!!
ReplyDeletethnk u
DeleteThanks to help
ReplyDeletewlcm
Delete